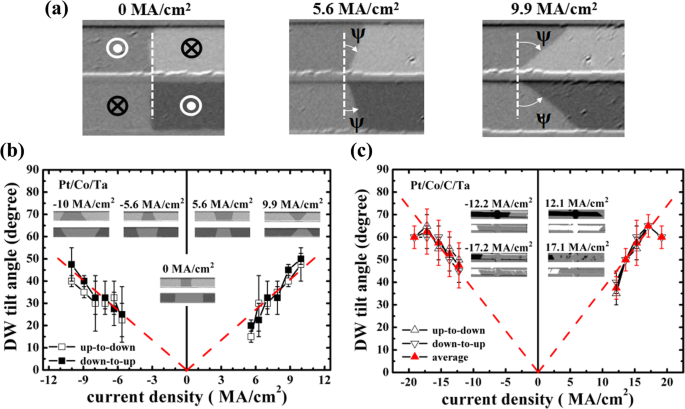
The boundary of the stripe domain region expands just like a domain wall when it is driven by a magnetic field and the velocity follows the creep law which is consistent with typical domain walls.
Magnetic domain wall strip.
Martinez current driven domain wall dynamics in ferromagnetic layers synthetically exchange coupled by a spacer.
Domain walls a bloch wall b neel wall c cross tie wall 2.
A micromagnetic study journal of applied physics 123 1.
Magnetic domains a uniaxial wall spacing b closure domain c stripe domains 3.
The strip consists of two uniformly magnetized domains separated by a bloch wall.
The period and magnetic layer thickness have obvious effect on the size of the stripe domain.
Magnetic knife strip 18 inch best kitchen magnetic knife holder wall knife magnet magnetic knife rack bar with 6 hooks in gift box 5 years guarantee 4 7 out of 5 stars 1 965 19 95 19.
A magnetic domain wall the boundary region between two magnetic domains with different magnetization orientations with nanoscale confinement can be considered as a particle trapped in a pinning potential well.
The project exploits the use of computer simulations to replicate a physical experiment.
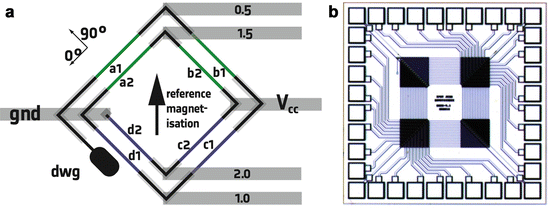
The strips are made with a curved shape to easily set a domain wall in the bent region after the application of an external magnetic field transverse to the strip 27 28.
The domain wall was driven by an applied magnetic field.
The boundary of the stripe domain region expand just like a domain wall when it is driven by magnetic field and the velocity follow the creep law which is consistent with the typical domain wall.
On the dynamics of the domain wall in a ferromagnetic strip.
In magnetism a domain wall is an interface separating magnetic domains it is a transition between different magnetic moments and usually undergoes an angular displacement of 90 or 180.
The domain wall thickness depends on the anisotropy of the material but on average spans across around 100 150 atoms.
Adapted from lin et al.
Magnetic domain and domain walls 1.
Magnetic domain and domain walls 1.
E field control of domain wall dynamics in cofeb.
The resulting magnetic.
Its dynamic response to external factors such as applied magnetic fields or electrical currents depend heavily on the structure of the domain wall.
The repeat number and magnetic layer thickness have an obvious effect on the size of the stripe domain.
A domain wall is a gradual reorientation of individual moments across a finite distance.
B differential kerr images of magnetic domain wall displacement under a magnetic field of 2 6 mt and gate voltages of 1 0 and 0 8 v.